Statistical tests are tools scientists use to spot important results – those rising above the randomness or “noise” in the universe. We use statistical tests in A-level biology because even if a change in our data “looks” dramatic by eye, the test provides the unbiased reassurance to make our conclusions confidently.
Statistical tests work by setting a threshold (called the probability value level, p-value level or confidence level) used to separate important changes from differences that could be explained by randomness in our measurements. Only data rising above this threshold gain the title “significant”.
But how do we know which statistical test to use?
Choosing statistical tests in A-level biology
Firstly, some good news – you don’t need to memorize any mathematical formulae! If you need them in the exam, they will be given to you. But you do need to know how and when use the tests. (And if you are with the OCR or Edexcel exam boards you may have to actually do some calculations.)
Which statistical test we use depends on which one best suits your data. We have a choice of three different statistical tests in A-level biology:
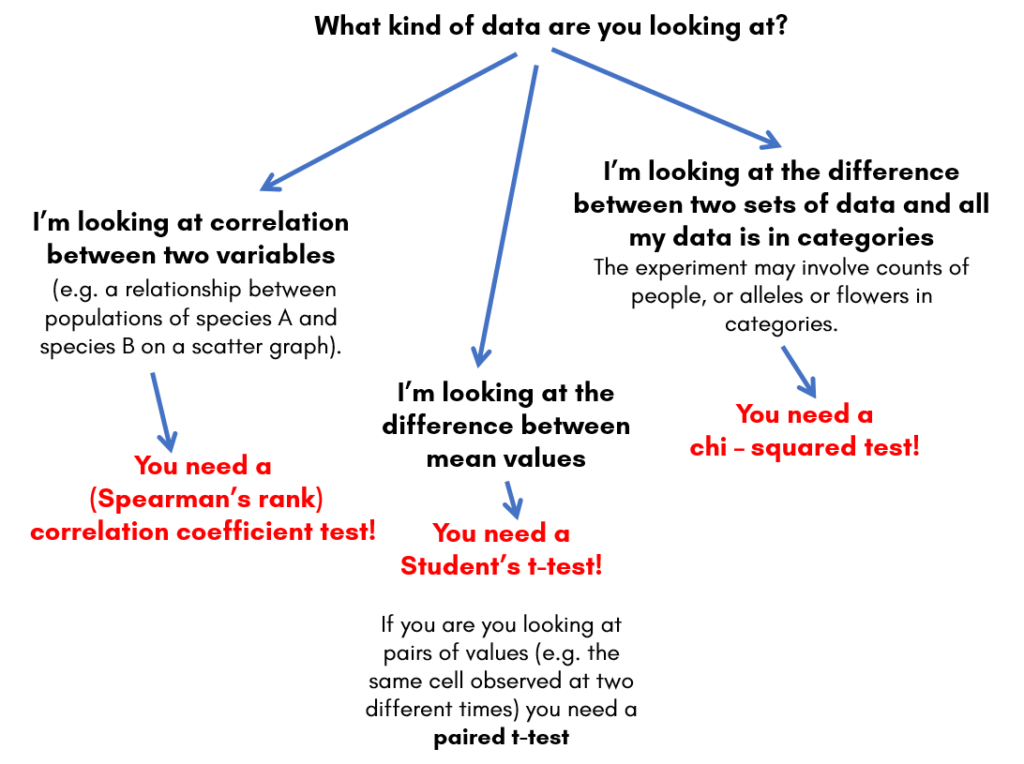
Chi-squared test – used when looking at differences between frequencies (data that is counted) in different categories (known as discrete data).
Student’s t-test – used to look at differences between means (averages) of data involving measurements (like lengths, or times).
Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient test– used to look at the correlation between two variables in measured data.
Here is a diagram to help you choose:
Examples of choosing statistical tests in A-level biology exam questions
Exam questions may present you with a situation – perhaps a scientist doing an experiment – and ask you to choose the appropriate statistical test. Here are some model answers to real A-level biology exam questions involving a
choice of test:
(While I cannot reproduce the questions here for copyright reasons, I have linked to the actual papers on the exam board websites.)
AQA 2022 paper 2 Q 6.5
This would require a Chi-squared test (as the data involves frequencies in categories).
AQA 2019 AS paper 2 Q8.4
This would require a t-test (this is tricky as the data presented involves frequencies, but the statistical test would be aimed at the difference between mean values – which are measurements, so it’s a t-test we need).
OCR 2022 biological processes paper Q9
We would choose B: The (unpaired) t-test. Unpaired because the data from light and dark are not related (i.e. they are not the same cells analysed different times) and a t-test because we would pool the data from cells in light vs dark areas to examine the difference between mean values.
Hopefully this helps with you choose between statistical tests in A-level biology exam questions! This blog is part of a larger study guide to A-level biology statistics (see below). I’ve also written about how to answer A-level biology evaluate questions, and application questions, but what about “Describe” and “explain” questions.
Good luck!
 There’s much more help with statistical tests, p-values, significance etc. (and model answers to statistics exam questions) in our eBook “How to use statistical tests in A-level biology”, available here.
There’s much more help with statistical tests, p-values, significance etc. (and model answers to statistics exam questions) in our eBook “How to use statistical tests in A-level biology”, available here.
If you’d like to work through some A-level biology statistics questions, from exam boards like AQA, please get in touch with me at Woolton Tutors, and we can set up some online A-level biology tutoring sessions. Alternatively, AQA students might be interested in my weekly A-level biology masterclass sessions for practice on exam technique.
Best wishes,
John
Dr John Ankers
Specialist online A-level biology tutor and academic wellbeing coach